Advanced container settings
When creating or editing a container you can configure a number of additional settings in the Advanced container settings section.
Command & logging
In this section you can configure the command that runs when the container starts as well as configure logging for the container.
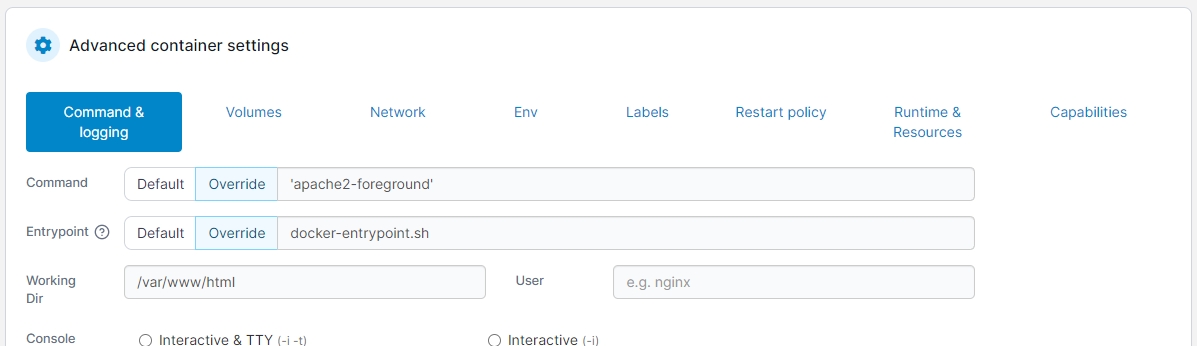
Command
Set the command that is run when the container starts. Select Default to use the default command provided by the container's image, or select Override and provide a command to override the default value.
Entrypoint
Set the entrypoint for the container. Select Default to use the default entrypoint provided by the container's image, or select Override and provide an entrypoint to override the default value.
Working Dir
Set the working directory your container should start in (within the container's filesystem).
User
Specify the user that the container's command should run as.
Console
Set the console configuration for your container.
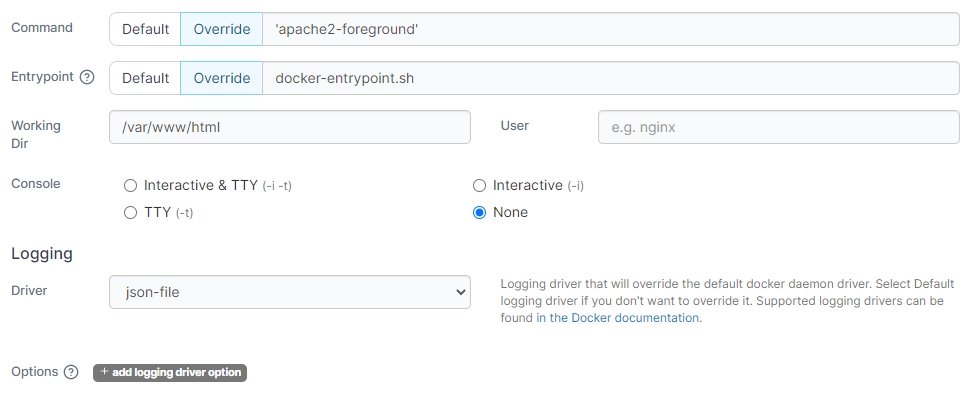
Driver
Select the logging driver to use for your container. Available options will depend on the logging drivers configured on your Docker host.
Options
Set additional options for your logging driver. To add a new option click add logging driver option and configure accordingly.
Volumes
Here you can configure volume mappings for your container. You can map to existing named volumes or bind mount to locations on your Docker host.
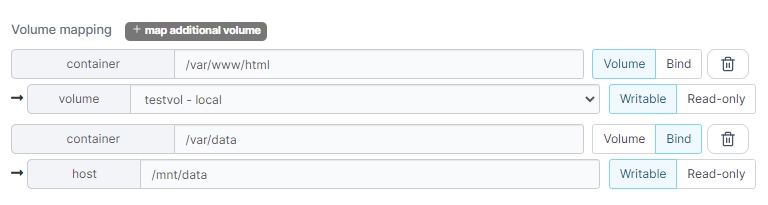
Container path
Specify where you want to make the volume or bind mount available within the container's filesystem.
Mapping type
Select Volume to map a named volume, or select Bind to map a bind mount.
Volume
If using the Volume mapping type, select the named volume to mount from the dropdown.
Host path
If using the Bind mapping type, specify the path on the Docker host you want to bind mount in the container.
Writable / Read-only
Select Writable if you want the container to be able to write to the mapping. Select Read-only if the container should not be able to write to the mapping.
Network
In this section you can configure the network settings for the container.
Note that you cannot assign a static IP address to a container that is in Docker's default bridge network. This is a Docker limitation rather than Portainer. If you need to specify the IP for your container then you will need to create a custom network and assign the container to it.
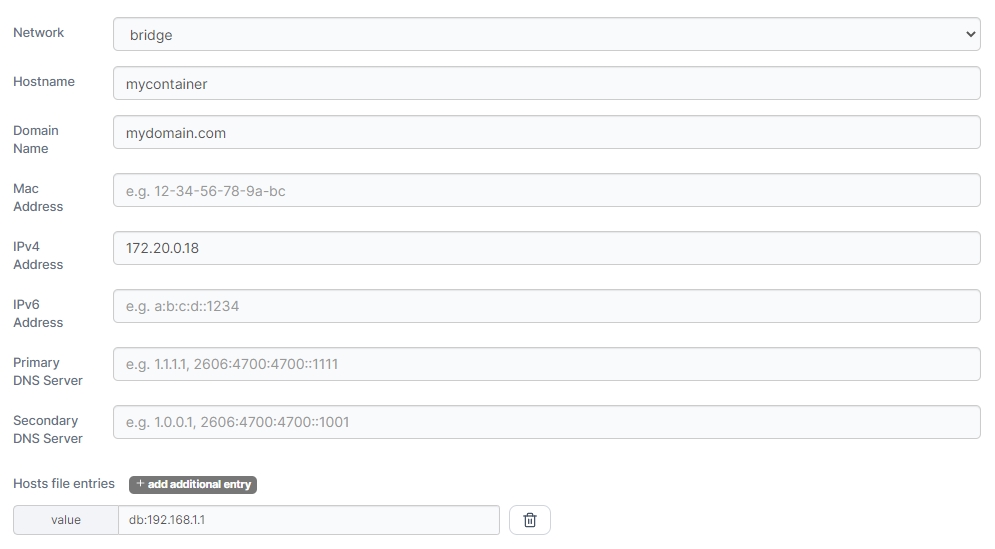
Network
Select the network to attach the container to from the dropdown.
Hostname
Specify the hostname for the container.
Domain Name
Specify the domain name for the container.
Mac Address
Specify the MAC address to set on the container.
IPv4 Address
Specify the IPv4 address to use for the container. This must be within the range for the chosen network and should not be already assigned to a container.
IPv6 Address
Specify the IPv6 address to use for the container. This must be within the range for the chosen network and should not be already assigned to a container.
Primary DNS Server
Specify the primary DNS server to use within the container.
Secondary DNS Server
Specify the secondary DNS server to use within the container.
Hosts file entries
Click add additional entry to add a new host file entry for the container. Host file values should be formatted as hostname:address (for example database:192.168.1.1).
Env
Use this section to add or edit environment variables made available in the container. Click Add an environment variable to create a new variable, or edit an existing variable with the fields provided. You can also click Load variables from .env file to import an existing .env file with your variables. To remove a variable, click the trash can icon to the right of the variable to remove.
Name
Set the name for the environment variable.
Value
Set the value for the environment variable.
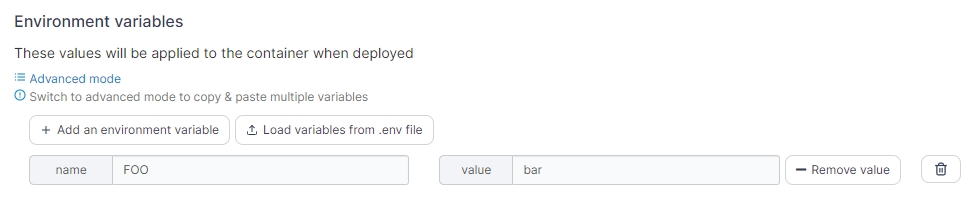
If you want to add multiple variables at once, click on Advanced mode to switch to an editor view where you can paste a block of variables and values.
Labels
You can set labels on your container using this section. Click add label to add a new label, or edit an existing label using the fields provided. To remove a label, click the trash can icon to the right of the label to remove.
Name
Set the name for the label.
Value
Set the value for the label.
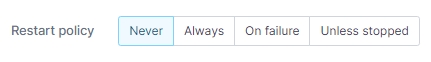
Restart policy
Use this section to configure the restart policy for your container. Possible options are:
Never: Do not automatically restart the container when it exits. This is the default.
Always: Always restart the container regardless of the exit status. When you specify always, Docker will try to restart the container indefinitely. The container will also always start on Docker startup, regardless of the current state of the container.
On failure: Restart only if the container exits with a non-zero exit status.
Unless stopped: Always restart the container regardless of the exit status, including on Docker startup, except if the container was put into a stopped state before Docker was stopped.
Runtime & Resources
This section lets you configure runtime options for your container, add or configure GPUs for use within the container, and specify resource limitations on the container.
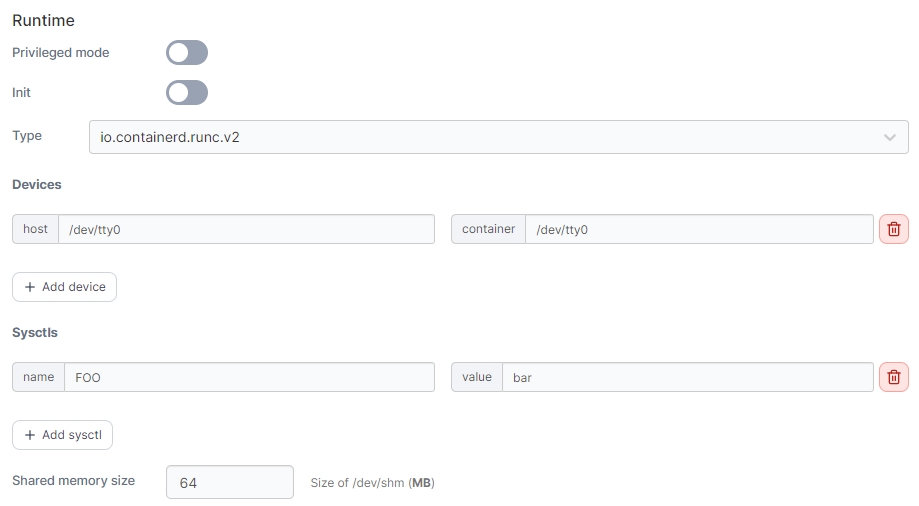
Runtime
Here you can configure runtime options for the container.
Privileged mode
Enable this option to run the container in privileged mode.
Init
Enable this option to tell Docker that an init process should be used as PID 1 in the container.
Type
Select the runtime type to use to start the container. Options will depend on available runtimes on your Docker host.
Devices
Use this option to make devices on your Docker host available within the container. Click add device to add a new device, and define the host path for the device and the container path for where you want the device to appear within the container.
Sysctls
Use this option to specify sysctls to make available within the container. Click add sysctl to add a new sysctl, and set the name and value for your sysctl as required.
Shared memory size
Specify the size (in MB) of the shared memory device (/dev/shm) for the container.
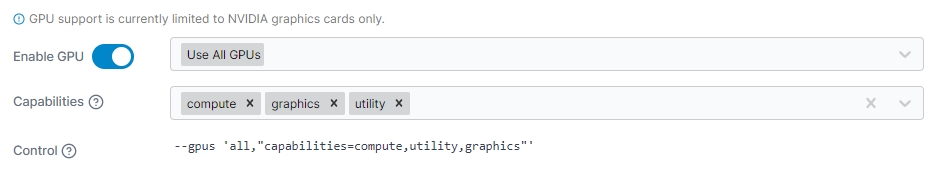
GPU
Here you can enable GPU access for the container and configure the GPU settings as required.
Enable GPU
Toggle this option on to enable GPU access for the container.
GPU selector
Select the GPU(s) to make available to the container, or choose Use All GPUs to provide access to all the GPUs on the Docker host.
Capabilities
Select the capabilities you want to use with the container. Portainer preselects compute and utility as they are the defaults when not specifying capabilities.
Control
View a generated equivalent of the Docker CLI's --gpus option based on your selections above.
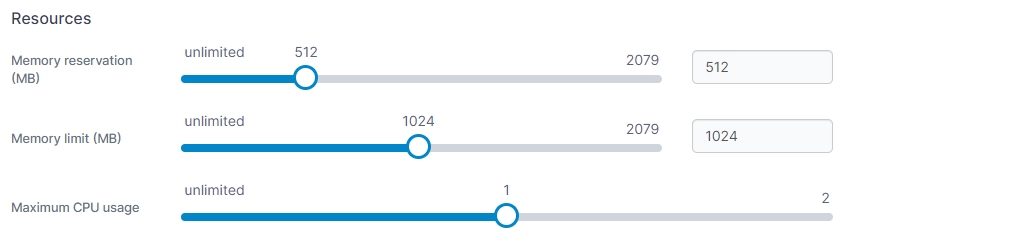
Resources
Here you can configure resource limits for your container. You can use the sliders to set the value or enter a value in the fields.
Memory reservation (MB)
Specify the amount of memory (in MB) to reserve for the container.
Memory limit (MB)
Specify the maximum amount of memory (in MB) the container is allowed to use.
Maximum CPU usage
Specify the maximum amount of CPU the container is allowed to use. This is specified based on the number of processing threads available on your Docker host.
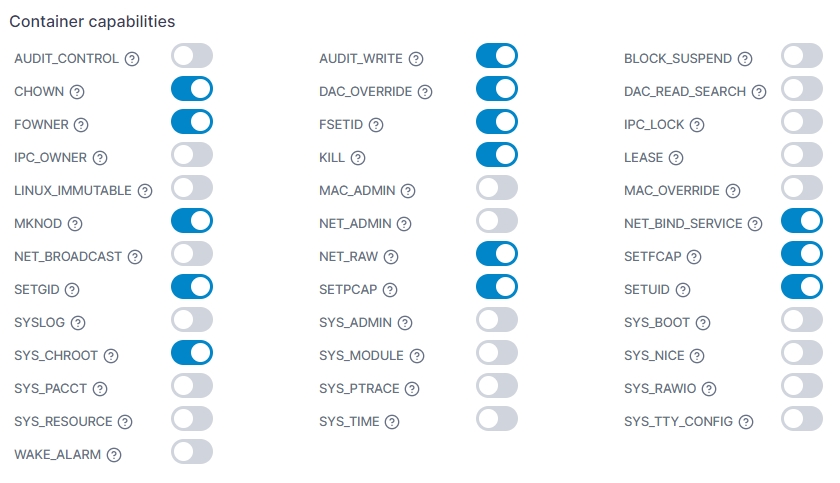
Capabilities
In this section you can configure the individual capabilities for your container. For more information refer to the Docker documentation.
Was this helpful?