Install Portainer BE with Kubernetes on WSL / Docker Desktop
These installation instructions are for Portainer Business Edition (BE). For Portainer Community Edition (CE) refer to the CE install documentation.
Introduction
The following instructions will guide you in setting up Portainer Server with Kubernetes running on Docker Desktop with WSL.
This scenario is for testing purposes only.
We are aware of an issue where namespace and application access privileges are not fully implemented when running Kubernetes via Docker Desktop. We are looking into the root cause and hope to have a resolution soon.
Preparation
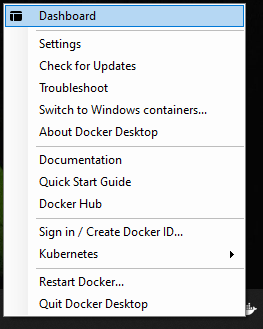
Before you start, you must make sure that Kubernetes is enabled and running within your Docker Desktop installation. To enable Kubernetes in Docker Desktop, you need to open the dashboard of Docker Desktop. Right click the Docker icon in the system tray and click Dashboard:
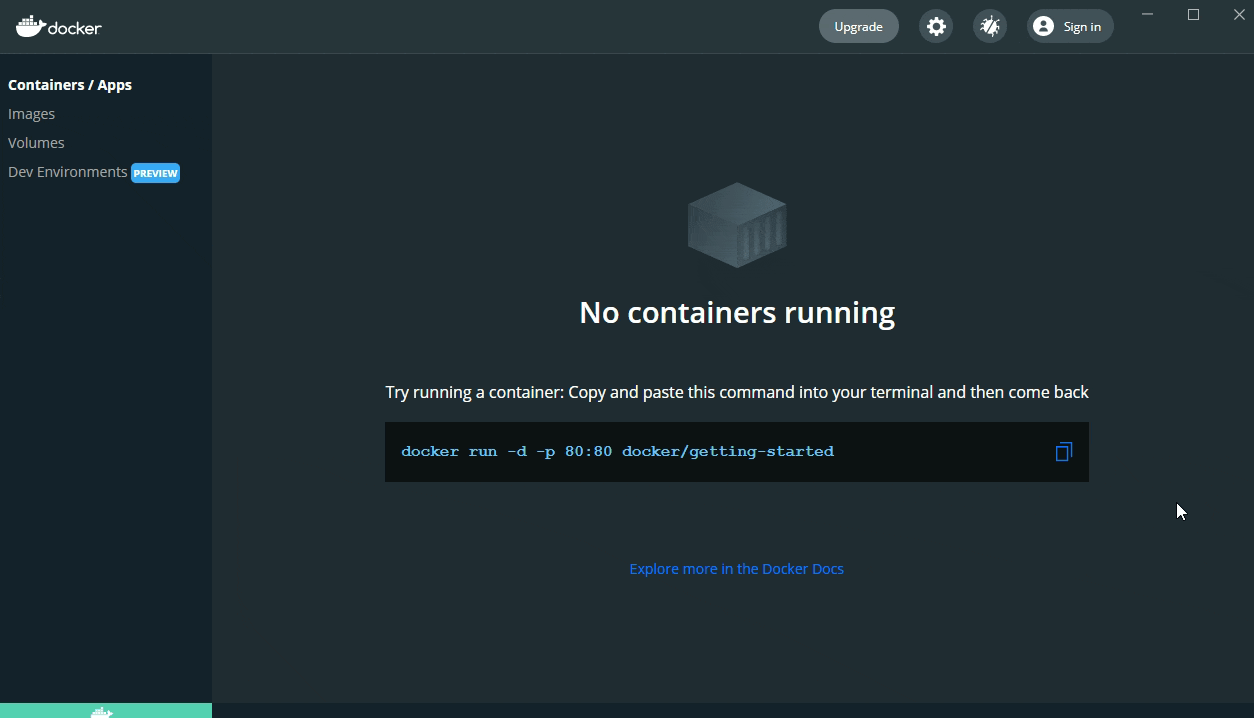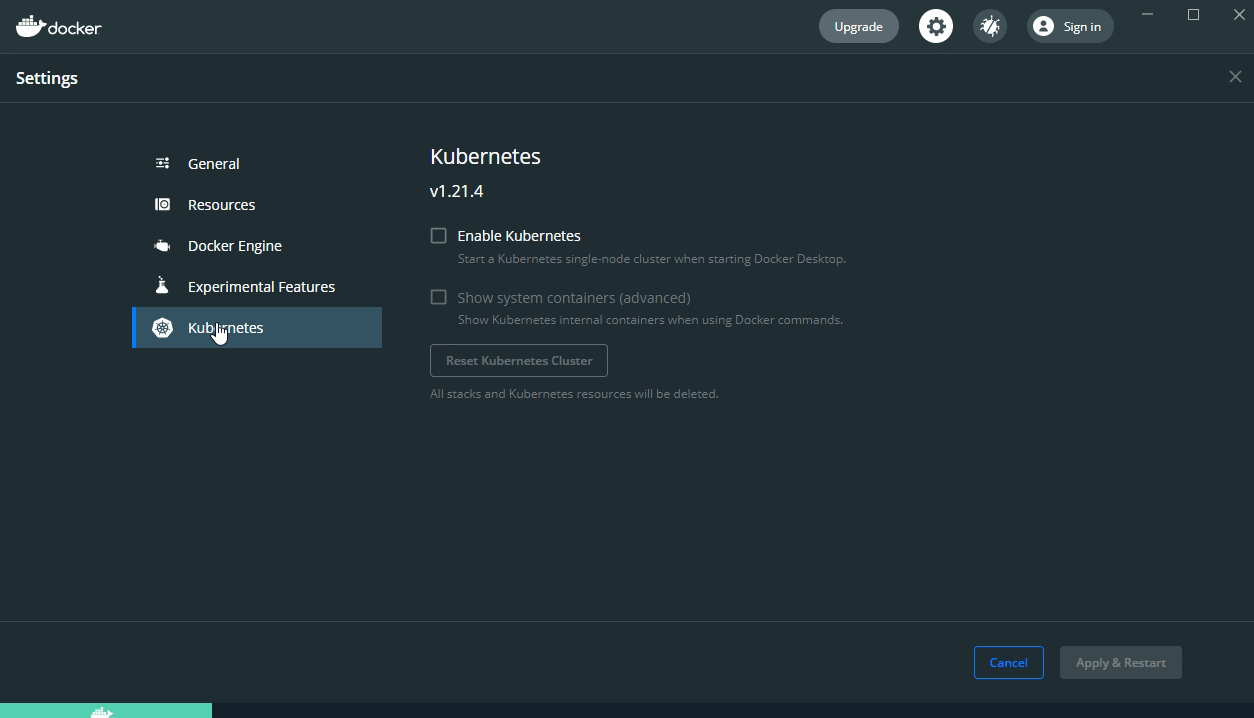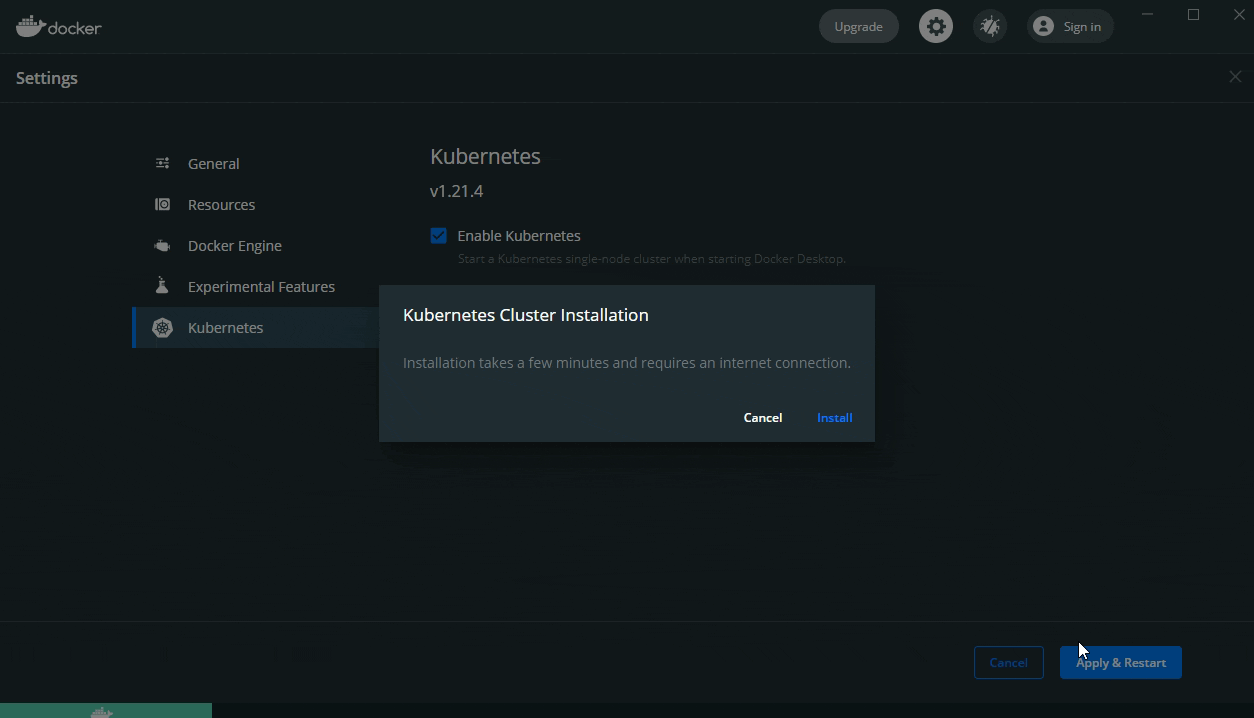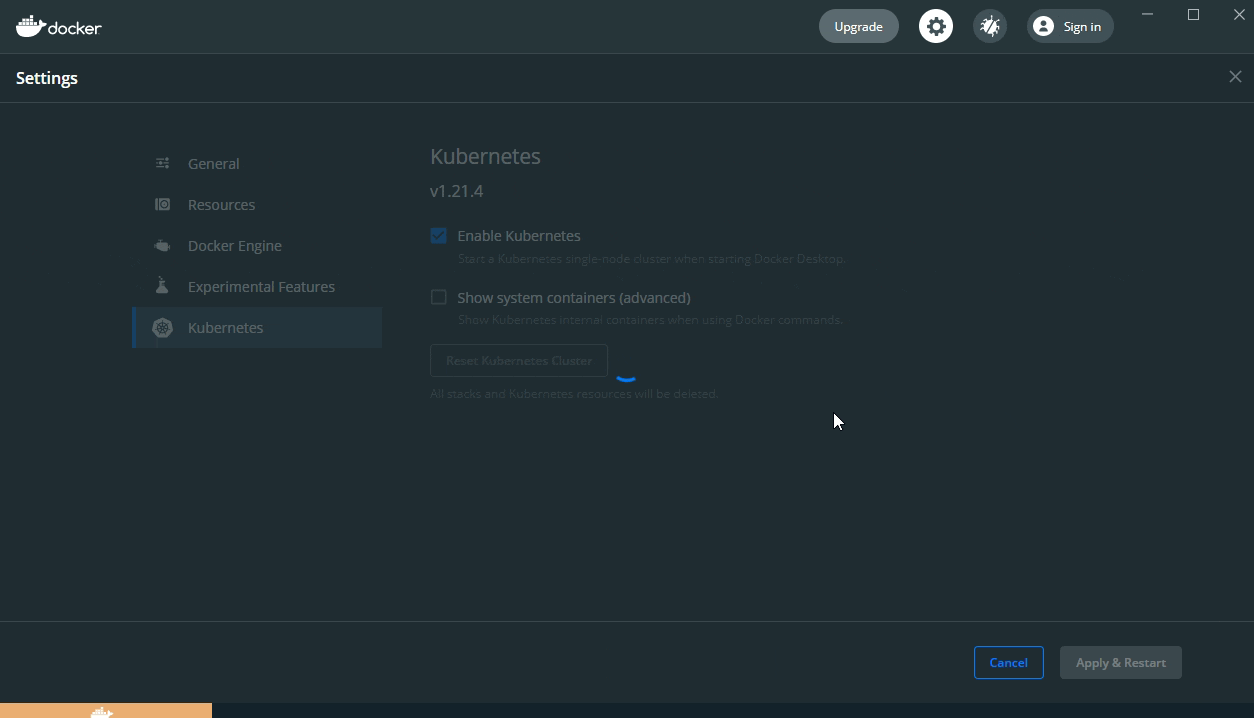
Click Settings, then select Kubernetes, tick Enable Kubernetes, then click Apply and Restart (clicking Install in the dialog to install Kubernetes):
After a few minutes, you will see that Kubernetes is running in the bottom left status bar of Docker Desktop:
Deployment
To deploy Portainer within a Kubernetes cluster you can use our provided Helm charts or YAML manifests.
Deploy using Helm
Ensure you're using at least Helm v3.2, which includes support for the --create-namespace argument.
First add the Portainer Helm repository by running the following commands:
Once the update completes, you're ready to begin the installation. Which method you choose will depend on how you wish to expose the Portainer service:
Using the following command, Portainer will be available on port 30777 for HTTP and 30779 for HTTPS:
By default, Portainer generates and uses a self-signed SSL certificate to secure port 9443. Alternatively you can provide your own SSL certificate during installation or via the Portainer UI after installation is complete.
In this example, Portainer will be deployed to your cluster and assigned a Cluster IP, with an nginx Ingress Controller at the defined hostname. For more on Ingress options, refer to the list of Chart Configuration Options.
Using the following command, Portainer will be available at an assigned Load Balancer IP on port 9000 for HTTP and 9443 for HTTPS:
By default, Portainer generates and uses a self-signed SSL certificate to secure port 9443. Alternatively you can provide your own SSL certificate during installation or via the Portainer UI after installation is complete.
To explicitly set the target node when deploying the Helm chart on the CLI, include --set nodeSelector.kubernetes.io/hostname=<YOUR NODE NAME> in your helm install command.
Deploy using YAML manifests
Our YAML manifests support exposing Portainer via either NodePort or Load Balancer.
To expose via NodePort, you can use the following command (Portainer will be available on port 30777 for HTTP and 30779 for HTTPS):
By default, Portainer generates and uses a self-signed SSL certificate to secure port 30779. Alternatively you can provide your own SSL certificate during installation or via the Portainer UI after installation is complete.
To expose via Load Balancer, use the following command to provision Portainer at an assigned Load Balancer IP on port 9000 for HTTP and 9443 for HTTPS:
By default, Portainer generates and uses a self-signed SSL certificate to secure port 9443. Alternatively you can provide your own SSL certificate during installation or via the Portainer UI after installation is complete.
To explicitly set the target node when deploying using YAML manifests, run the following one-liner to "patch" the deployment, forcing the pod to always be scheduled on the node it's currently running on:
Logging In
Now that the installation is complete, you can log into your Portainer Server instance. Depending on how you chose to expose your Portainer installation, open a web browser and navigate to the following URL:
Replace localhost with the relevant IP address or FQDN if needed, and adjust the port if you changed it earlier.
Replace <FQDN> with the FQDN of your Portainer instance.
Replace <loadbalancer IP> with the IP address or FQDN of the load balancer, and adjust the port if you changed it earlier.
You will be presented with the initial setup page for Portainer Server.
Initial setupWas this helpful?